EFFICACY
SOMATULINE® DEPOT: MAINTAINED REDUCTION OF GH AND NORMALIZATION OF
IGF-11
For the long-term treatment of adult patients with acromegaly who had inadequate response to or cannot be treated with surgery and/or radiotherapy1
Efficacy in the 1-year pivotal trial1,2
DESIGN
ENDPOINT
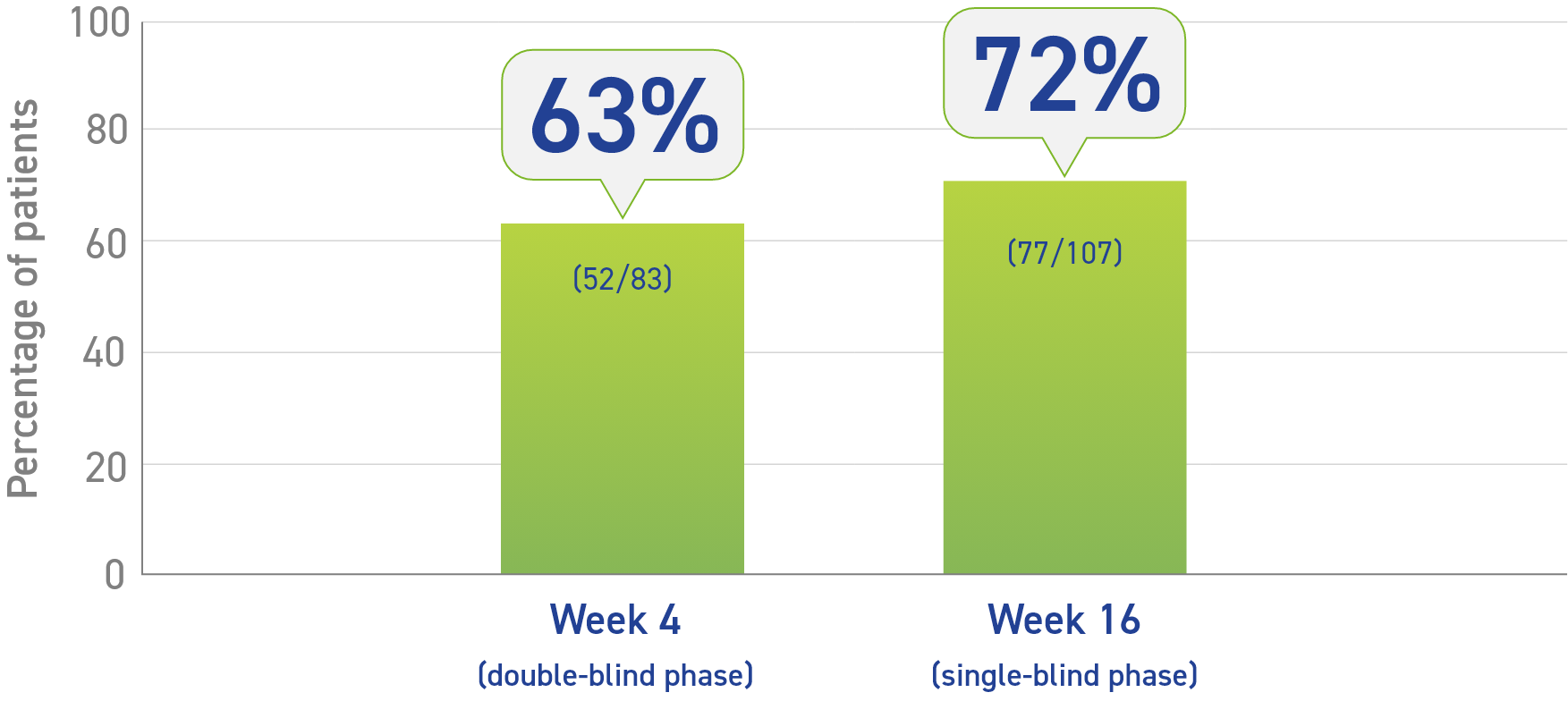
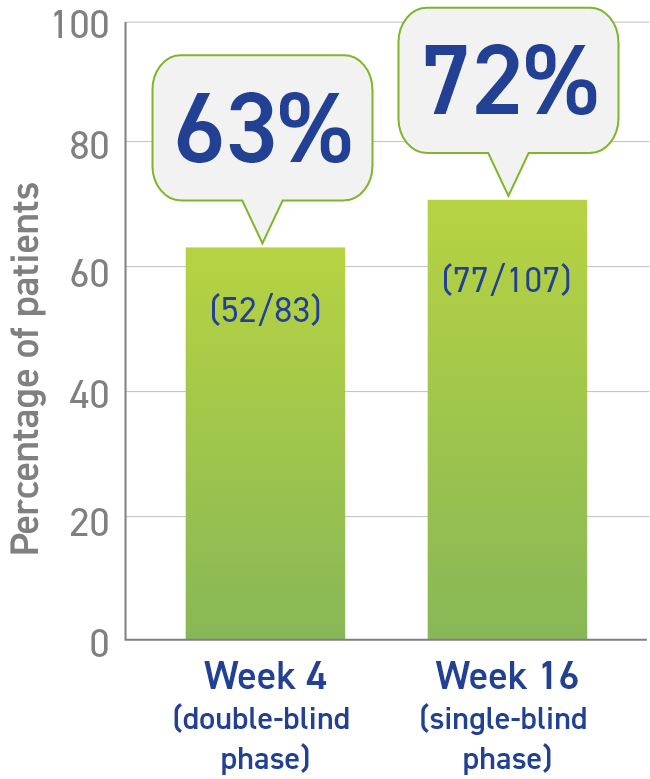
- Primary data: 4-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase1
- 63% of Somatuline® Depot patients (52/83) achieved >50% decrease of GH vs 0% of placebo patients (0/25)2
ENDPOINTS
- Secondary data: 16-week, single-blind, fixed-dose phase1
- At Week 16, 72% of patients had a >50% reduction in GH levels from baseline1
- Efficacy achieved in the first 16 weeks was maintained through 52 weeks1
- 82% of patients experienced >50% reduction in GH at
Week 52 (81/99)2
Percentage of patients who achieved a >50% decrease in growth hormones (GH)1,2

Adverse reactions in >5% of patients who received Somatuline® Depot were diarrhea (37%), cholelithiasis (20%), abdominal pain (19%), nausea (11%), and injection-site reactions (9%).1
Please also see the trial study design above and Patient Information below.
IGF-1 normalization responders1,2
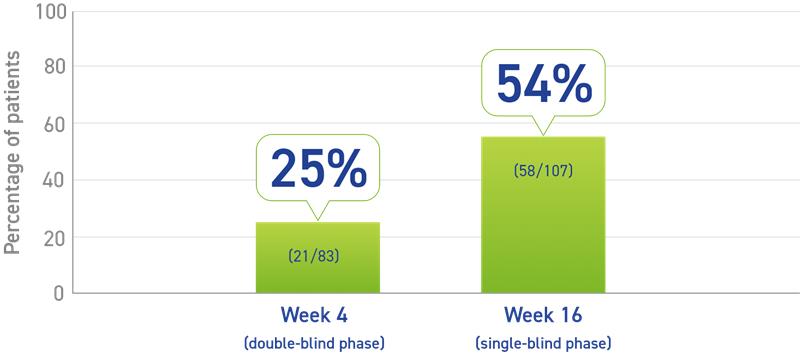
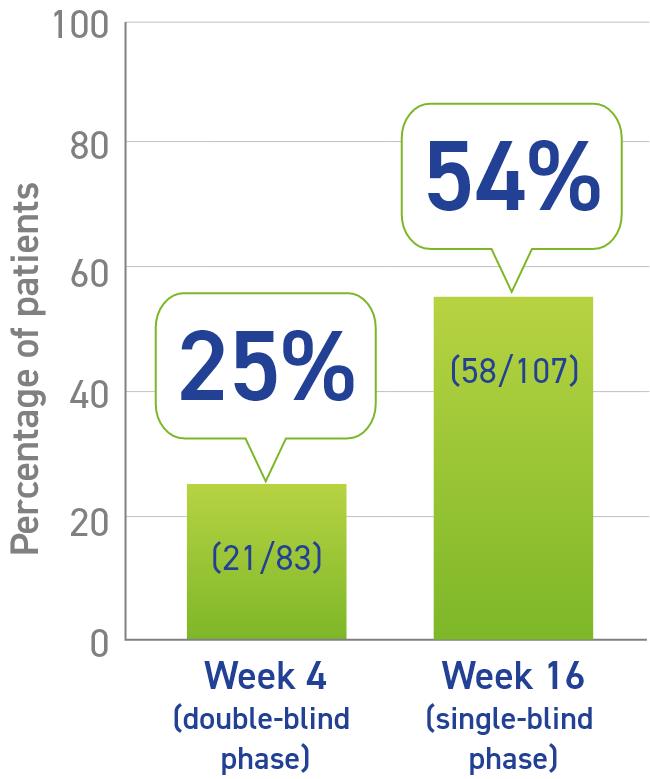
- Primary data:
- 25% of patients had normal IGF-1 levels after one injection2
- Secondary data:
- 54% of patients experienced IGF-1 normalization at Week 161
- 59% of patients experienced IGF-1 normalization at Week 522
Percentage of patients who experienced IGF-1 normalization responders1,2
Additional data
Extended dosing intervals (EDIs)1,3
Somatuline Depot was the first somatostatin analog (SSA) to offer FDA-approved EDI for controlleda patients1,3b
Biochemical control was maintained with 120-mg dosing administered once every 6 or 8 weeks3
aControlled is defined as GH level from >1.0 ng/mL to ≤2.5 ng/mL, normalized IGF-1 level, and satisfactory management of clinical symptoms as determined by the healthcare professional.1
bPatients who are controlled with Somatuline Depot 60 mg or 90 mg administered every 4 weeks can be considered for treatment with 120 mg administered every 6 or 8 weeks. GH and
IGF-1 levels should be obtained 6 weeks after this change in dosing regimen to evaluate persistence of patient response. Continued monitoring of patients’ response with dose adjustments for biochemical and clinical symptom control, as necessary, is recommended.1
Study design: In an open-label, comparative, multicenter, phase 3 trial, Somatuline Depot (lanreotide) Injection 120 mg was administered every 4, 6, or 8 weeks in patients previously receiving lanreotide microparticles every 5-7,
8-11, or 12-16 days, respectively.3,4 Of patients whose levels were controlled (GH ≤2.5 ng/mL and normalized IGF-1) when switched to extended dosing intervals (n=32), 5 out of 6 remained controlled after 3 injections at 6-week intervals and 23 out of 26 remained controlled after 3 injections at 8-week intervals.3,5
Pharmacokinetic (PK) profile during EDIs6
Serum concentration (Cmin) of lanreotide after a single deep subcutaneous injection in healthy volunteers (mean ± SD)6

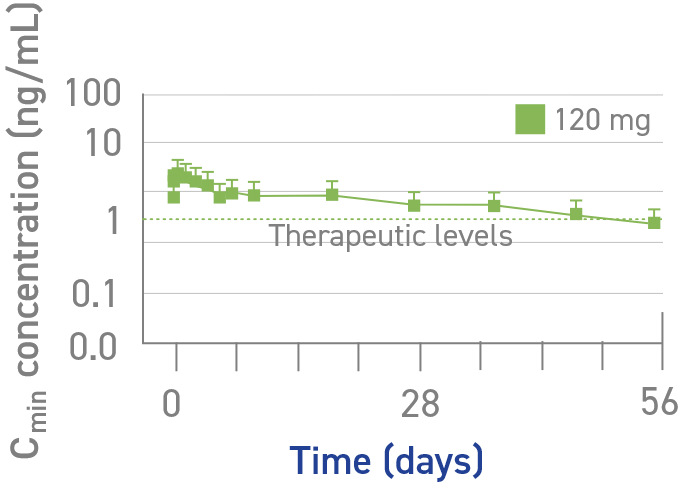
Study design: In a phase 1, single-center, open-label, randomized, parallel-group study, the pharmacokinetic profile of a single injection of lanreotide was assessed in healthy volunteers at a dose of 120 mg (n=12) through 56 days (8 weeks).7
In patients treated with Somatuline Depot 120 mg:
- Serum concentration (Cmin) through 6- and 8-week dosing intervals3
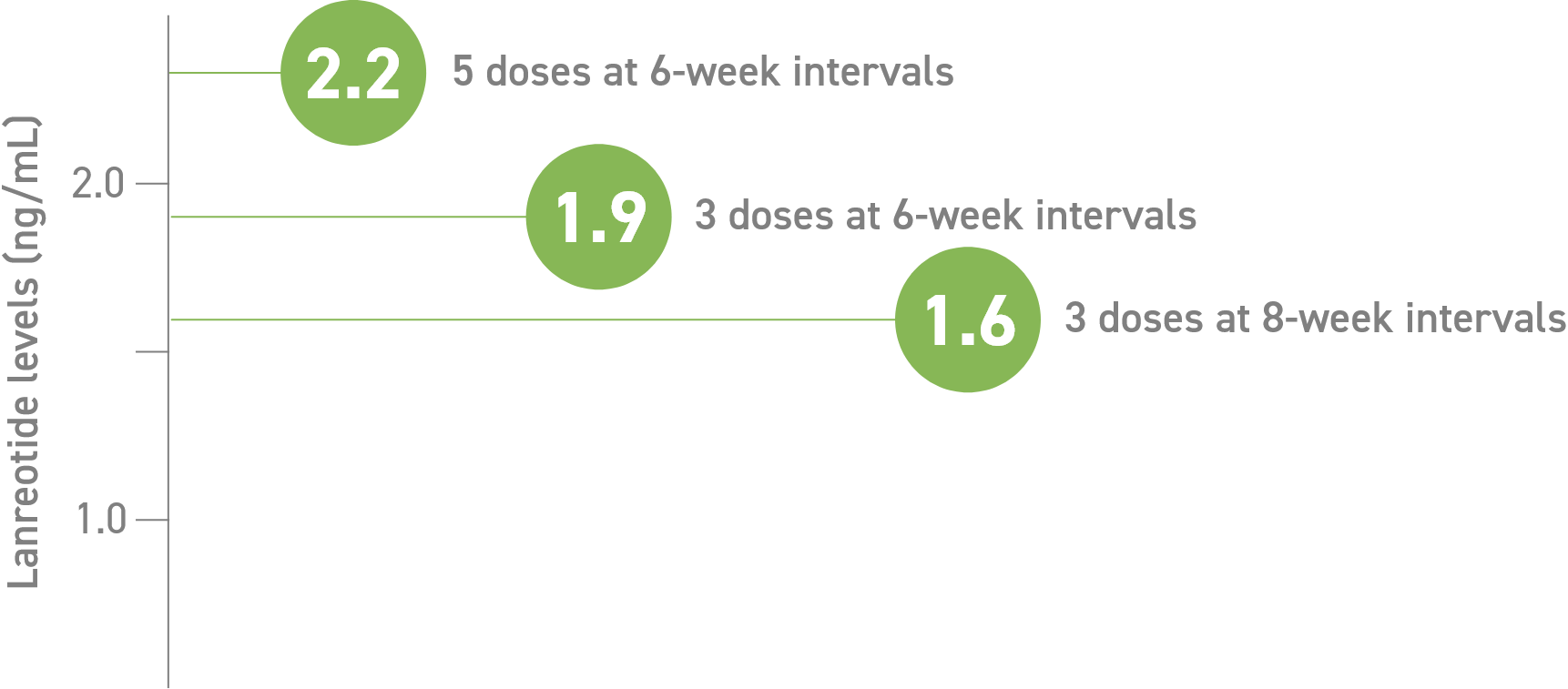
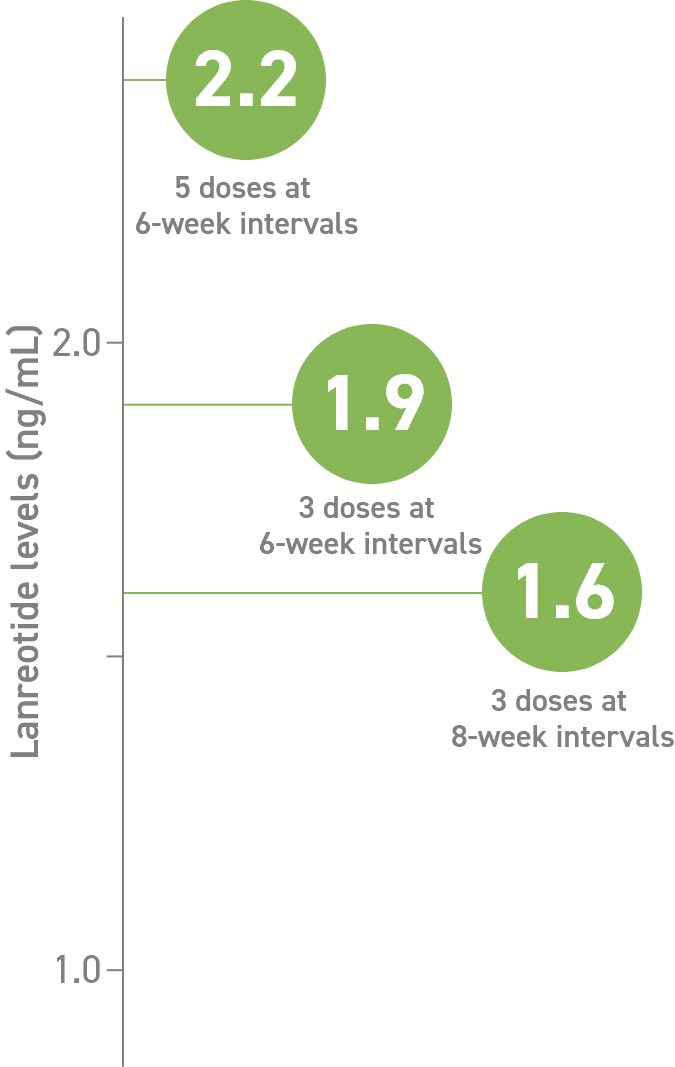
Study design: In open-label, comparative, multicenter, phase 3 trials, eligible patients who responded to SSAs received 3 to 5 injections of Somatuline
Depot 120 mg. Somatuline Depot 120 mg was injected every 4, 6, or 8 weeks in patients previously receiving lanreotide microparticles every 5-7, 8-11, or 12-16 days, respectively. There was no washout period or dose titration.3,4
FDA=Food and Drug Administration; GH=growth hormone; IGF-1=insulin-like growth factor 1; SD=standard deviation; SSA=somatostatin analog.
REFERENCES:
- Somatuline Depot (lanreotide) Injection [Prescribing Information]. Cambridge, MA: Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc; July 2024.
- Melmed S, Cook D, Schopohl J, et al. Rapid and sustained reduction of serum growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with acromegaly receiving lanreotide Autogel therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study with a 52 week open extension. Pituitary. 2010;13(1):18-28.
- Data on file. Ipsen Group. Serum Flashcard.
- Lucas T, Astorga R; Spanish–Portuguese Multicentre Autogel Study Group on Acromegaly. Efficacy of lanreotide Autogel® administered every 4–8 weeks in patients with acromegaly previously responsive to lanreotide microparticles 30 mg: a phase III trial. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006;65:320-326.
- Gomez-Panzani E, Chang S, Ramis J, et al. Sustained biochemical control in patients with acromegaly treated with lanreotide depot 120 mg administered every 4 weeks, or an extended dosing interval of 6 or 8 weeks: a pharmacokinetic approach. Res Rep Endocr Disord. 2012;2:79-84.
- Data on file. Ipsen Group. 2.7.2 Summary of Clinical Pharmacology Studies.
- Trocóniz IF, Cendrós JM, Peraire C, et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of lanreotide Autogel in healthy subjects: evidence for injection interval of up to 2 months. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(1):51-62.