- ADMINISTRATION
- Formulation
SOMATULINE® DEPOT IS A DEEP SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION WITH ONCE-MONTHLY DOSING VIA A STERILE, READY-TO-USE, SINGLE-DOSE, PRE-FILLED SYRINGE1,2
SOMATULINE® DEPOT
IS A DEEP
SUBCUTANEOUS
INJECTION WITH
ONCE-MONTHLY
DOSING VIA A STERILE,
READY-TO-USE, SINGLE-
DOSE, PRE-FILLED
SYRINGE1,2

The formulation of Somatuline Depot enables steady release without the need for polymers or additives.2

High density of lanreotide nanotubes allows for low injection volume.2
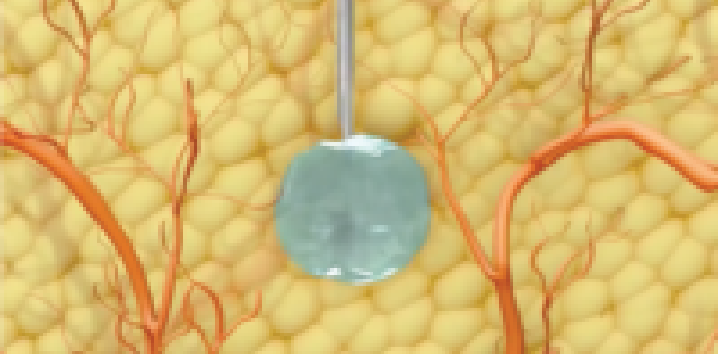
Lanreotide is injected into the deep subcutaneous layer of the tissue. After injection, the formulation is thought to form a depot – or drug reservoir, for fast-acting (peak serum concentration of 7 hours) and sustained-release (half-life of 23 to 30 days) drug delivery.1,2

Lanreotide is slowly released, enabling delivery every 4 weeks.2
Somatuline Depot, a rapid onset of action and sustained-release formulation1,2
Somatuline Depot has been shown to reach peak serum concentration in 7 hours, followed by a steady and sustained release (half-life of 23 to 30 days)1,2
Serum concentrations achieved in healthy subjects following deep SC administration of Somatuline Depot2

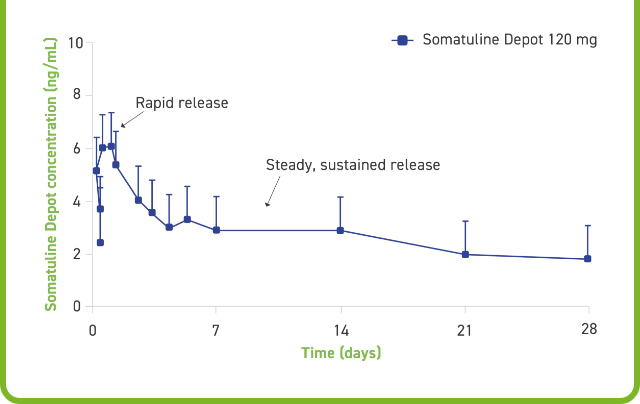
SC=subcutaneous.
REFERENCES:
- Somatuline Depot (lanreotide) Injection [Prescribing Information]. Cambridge, MA: Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc.; July 2024.
- Wolin EM, Manon A, Chassaing C, et al. Lanreotide depot: an antineoplastic treatment of carcinoid or neuroendocrine tumors. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2016;47(4):366-374.

